by staatse | Sep 27, 2024 | API Security, Application Security, Cybersecurity, IT Security Services, Penetration Testing
An API (Application Programming Interface) is essential for communication between different software systems. API pentesting is a process that identifies security vulnerabilities in these interfaces, helping prevent attackers from exploiting them. This guide provides an overview of API pentesting, common API types, and examples of various API architectures.
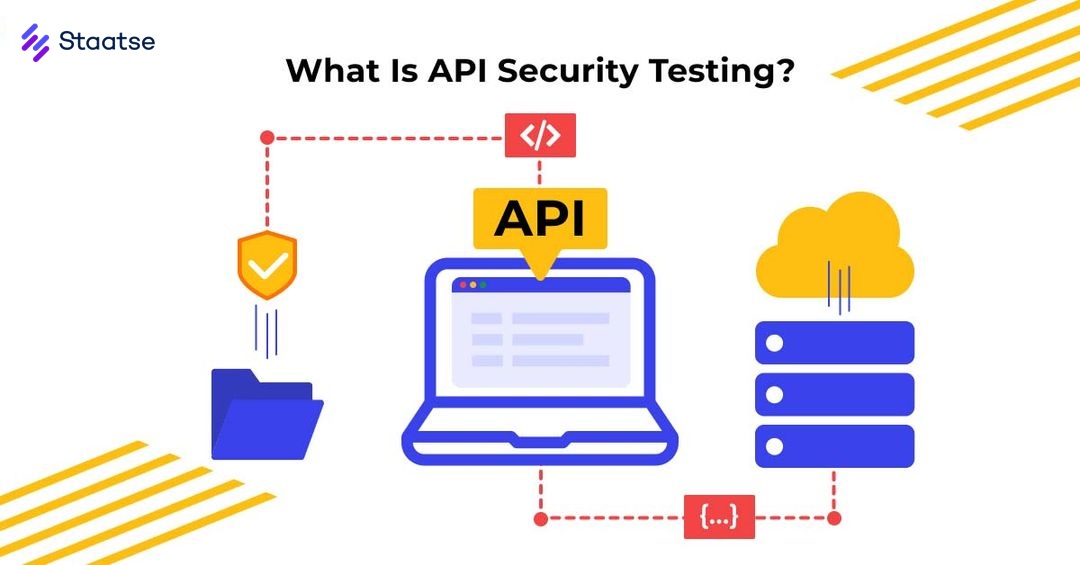
What is API Pentesting?
API pentesting involves testing APIs for security weaknesses such as:
- Injection attacks (e.g., SQL or XML injection)
- Sensitive data exposure
- Broken object-level authorization (BOLA)
- Broken function-level authorization (BFLA)
Pentesters simulate attacks to identify vulnerabilities, helping secure APIs before attackers can exploit them.
Importance of API Pentesting
- Identifying Security Vulnerabilities: APIs are common targets for security breaches. Pentesters identify potential vulnerabilities and recommend mitigation strategies.
- Protecting Sensitive Data: APIs handle sensitive data like passwords, personal information, and financial details. A breach can lead to data theft, financial losses, and damage to the organization’s reputation.
- Preventing Unauthorized Access: APIs often expose data to external users. Pentesting helps assess access control mechanisms to ensure only authorized users can interact with the API.
- Maintaining Business Continuity: Regular pentesting ensures APIs are secure, avoiding downtime or service interruptions caused by security incidents.
- Defense in Depth: API pentesting is part of a larger security strategy, adding multiple layers of defense against attacks.
Common API Types
APIs come in several forms, each with its security considerations:
- Public APIs: Open to external developers, but require proper authentication and authorization to prevent misuse.
- Partner APIs: Accessible only to authorized partners and require strong authentication and access control mechanisms.
- Private APIs: Used internally within organizations. While often protected by network-level security, they should still be pentested to ensure robustness.
- Composite APIs: Combine multiple services into one. They improve performance but may introduce security challenges that need thorough testing.
Popular API Architectures
1. RESTful API
RESTful APIs (Representational State Transfer) follow specific principles, focusing on statelessness, resource-based operations, and standardized HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE).
2. SOAP API
SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) is a messaging protocol that uses XML for exchanging structured information. It supports multiple transport protocols (HTTP, HTTPS, SMTP) and provides advanced security features like message encryption, digital signatures, and authentication.
Differences Between REST, SOAP, and GraphQL
- REST: Simple, stateless operations using HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE).
- SOAP: Strict and secure messaging protocol that uses XML and supports various transport protocols.
- GraphQL: Allows clients to request exactly the data they need, avoiding over-fetching and under-fetching issues.
Conclusion
API pentesting is essential for securing modern applications. Regular testing helps identify vulnerabilities, ensuring that sensitive data is protected, access controls are enforced, and the APIs are robust enough to withstand attacks. Stay tuned for Part 2, where we’ll dive into specific pentesting tools and techniques to secure APIs.
by staatse | Sep 19, 2024 | Application Security, Cybersecurity, Network Security, Penetration Testing, Vulnerability Management
In today’s digital landscape, businesses of all sizes depend heavily on technology to manage operations, store sensitive data, and engage with customers. This reliance, however, also increases the risk of cyber threats. To protect your business from potential attacks and data breaches, it’s crucial to implement strong security measures, and penetration testing is a key component of this defense strategy. But why is penetration testing so essential for your business? Let’s explore.
1. Identifying Vulnerabilities Before Attackers Do
- Proactive Detection: By simulating real-world attack scenarios, penetration testing can reveal vulnerabilities such as outdated software, weak passwords, or unsecured endpoints that cybercriminals could exploit.
- Comprehensive Assessment: It goes beyond traditional security measures, providing a thorough evaluation of your digital environment’s resilience against sophisticated attacks.
2. Enhancing Security Measures and Reducing Risk
Once vulnerabilities are identified, your business can take proactive steps to address these weaknesses. This not only strengthens your defenses but also reduces the risk of a successful cyberattack, protecting your sensitive data and maintaining business continuity.
- Tailored Security Improvements: Based on the findings, you can implement specific security measures such as applying patches, updating configurations, or enhancing monitoring practices.
- Risk Mitigation: Understanding the potential impact of each vulnerability allows you to prioritize and address the most critical issues first, reducing the overall risk to your organization.
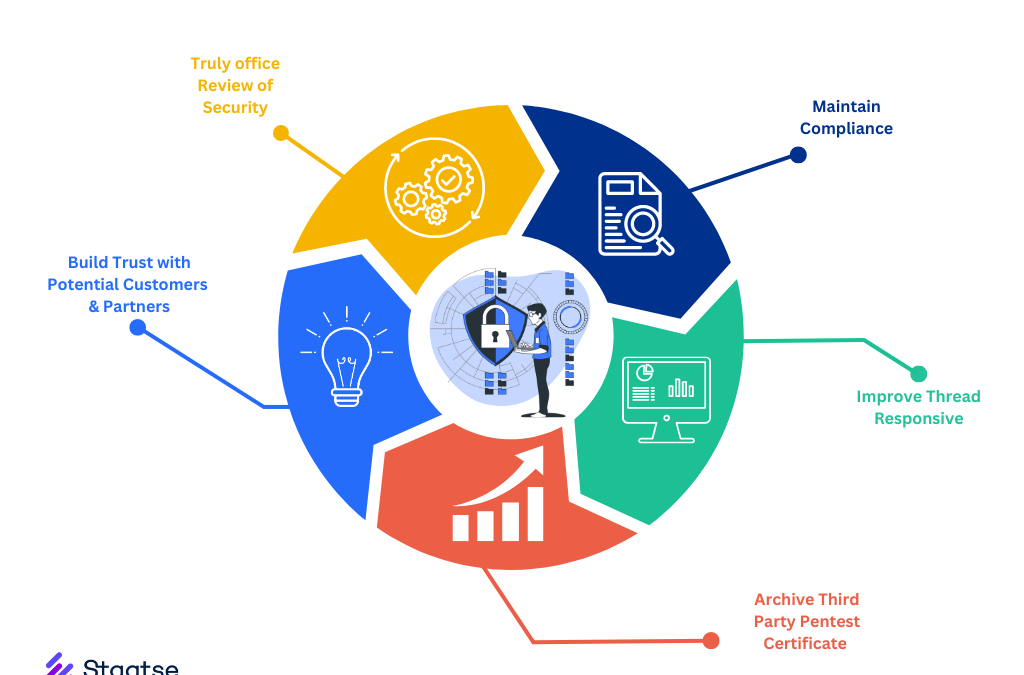
3. Ensuring Compliance with Industry Regulations
Many industries are governed by strict regulatory standards, such as GDPR for data protection, HIPAA for healthcare, and PCI-DSS for payment card security. These regulations often require regular security assessments, including penetration testing, to ensure that sensitive information is adequately protected.
- Meeting Compliance Requirements: Regular penetration testing helps demonstrate your commitment to maintaining a high level of security and ensures that your business complies with industry-specific regulations.
- Avoiding Legal and Financial Penalties: Failing to comply with these regulations can result in significant fines and legal consequences. Penetration testing helps you avoid such risks by identifying and addressing potential compliance gaps.
4. Protecting Your Reputation and Building Trust
A data breach can have a devastating impact on your company’s reputation, leading to loss of customer trust, reduced revenue, and long-term damage to your brand. Penetration testing is a proactive measure that shows your commitment to cybersecurity, helping to build trust with customers, partners, and stakeholders.
- Customer Confidence: By proactively securing your systems, you reassure customers that their data is safe and that your business is a trustworthy partner.
- Brand Protection: Preventing breaches before they occur helps safeguard your brand’s reputation, avoiding the negative publicity and loss of trust associated with security incidents.
How to Implement Penetration Testing: A Step-by-Step Guide
1. Define Clear Objectives
Identify what you aim to achieve with penetration testing. Are you focusing on a specific application, network segment, or your entire IT infrastructure? Clearly defining your goals will help tailor the testing to your specific needs and ensure meaningful results.
2. Choose the Right Testing Approach
There are different methodologies to choose from:
- Black Box Testing: The tester has no prior knowledge of the system, simulating an external attack.
- White Box Testing: The tester has full access to the system’s architecture and source code, allowing for a comprehensive security evaluation.
- Gray Box Testing: The tester has partial knowledge of the system, representing a scenario where an insider or semi-privileged user might attack.
Select the approach that best aligns with your security objectives and budget.
3. Select a Reliable Penetration Testing Provider
Choose a reputable provider with experience in your industry. Look for a company that offers a structured approach, detailed reporting, and a clear plan for post-testing support. Ask for case studies or references to ensure they have a proven track record.
4. Conduct the Testing
During the testing phase, the penetration testing team will simulate attacks on your systems, identifying vulnerabilities and assessing their potential impact. They will then provide a comprehensive report detailing the findings, along with recommendations for remediation.
5. Address and Mitigate Vulnerabilities
The final step is to act on the findings from the penetration test. This might involve applying security patches, updating configurations, revising access controls, or implementing additional security measures. Regular follow-up testing can ensure that these vulnerabilities have been effectively addressed.
Conclusion
Penetration testing is a strategic investment that helps protect your business from the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats. By proactively identifying and addressing security vulnerabilities, you not only enhance your defenses but also ensure compliance with industry regulations, protect your reputation, and build trust with your customers. In a digital world where security breaches are increasingly common, penetration testing is a crucial tool for maintaining a secure and resilient business environment.



