March 2025 Zero-Day Vulnerability Report

Introduction:
In March 2025, several critical zero-day vulnerabilities were identified and addressed by major software vendors, including Microsoft and Adobe. This report highlights the key vulnerabilities, their potential impacts, industry-specific insights, and practical advice for small businesses.
Microsoft Patches:
Microsoft released patches for 56 new CVEs, including six critical vulnerabilities and 50 important ones. Notably, six zero-day vulnerabilities were actively exploited in the wild. Key vulnerabilities include:
-
CVE-2025-26633: A security feature bypass in Microsoft Management Console, actively exploited.
-
CVE-2025-24985: A remote code execution vulnerability in the Windows Fast FAT File System Driver.
Adobe Patches:
Adobe addressed 37 CVEs across multiple products, including Acrobat Reader, Illustrator, and InDesign. Critical vulnerabilities in these products could allow attackers to execute arbitrary code.
Industry-Specific Data:
-
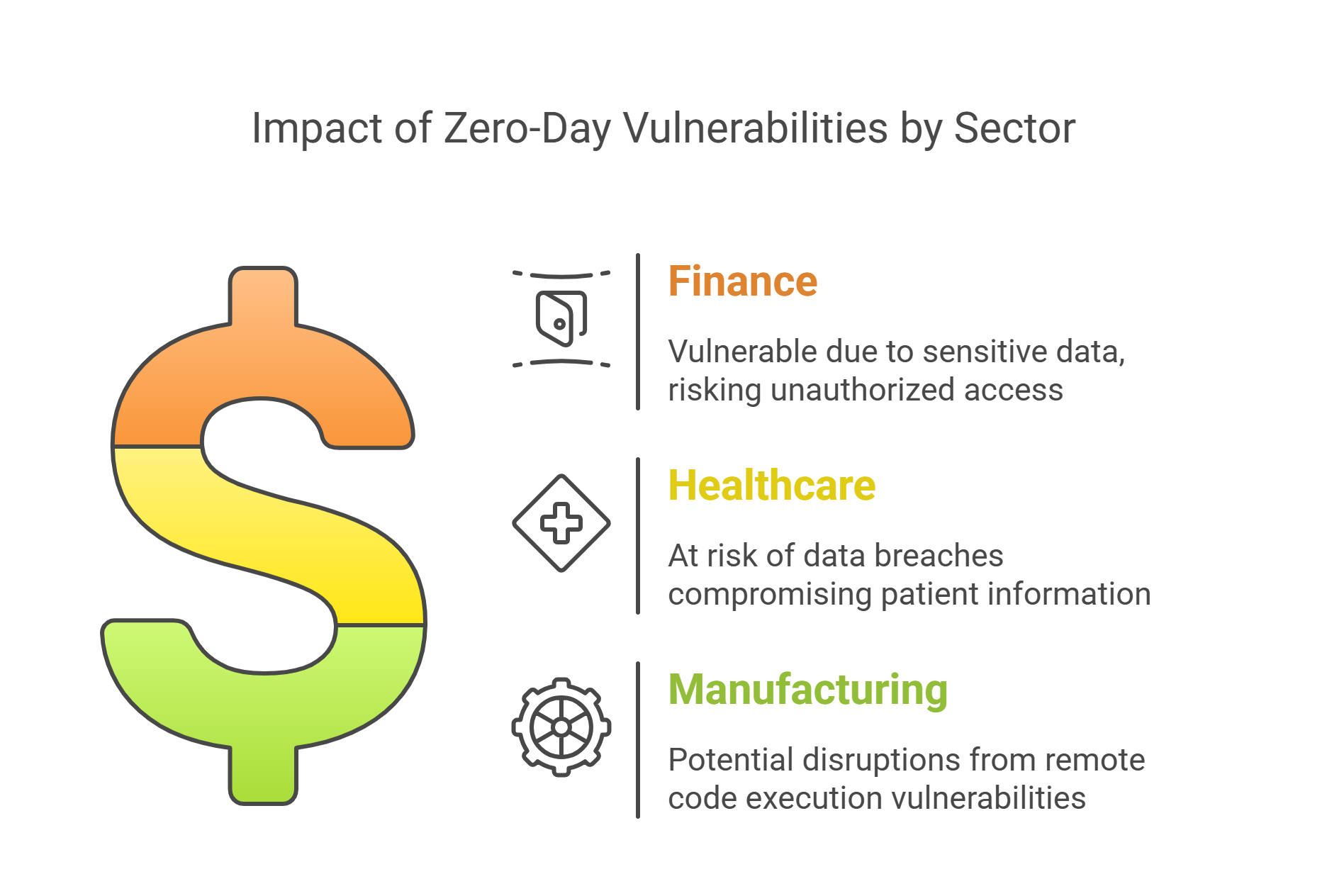
Finance: Financial institutions are particularly vulnerable to zero-day exploits due to the sensitive nature of their data. The CVE-2025-26633 vulnerability could allow attackers to bypass security features and gain unauthorized access to financial systems.
-
Healthcare: The healthcare sector, with its reliance on electronic health records, is at risk from vulnerabilities like CVE-2025-24985, which could lead to data breaches and compromise patient information.
-
Manufacturing: Manufacturing industries using Windows-based systems for automation and control could be affected by remote code execution vulnerabilities, potentially disrupting operations.
Implications of These Vulnerabilities:
Zero-day vulnerabilities pose significant risks as they are exploited before patches are available. The implications include:
-
Data Breaches: Unauthorized access to sensitive data.
-
Operational Disruption: Interruption of business operations and services.
-
Financial Loss: Costs associated with data breaches, including fines and remediation efforts.
-
Reputation Damage: Loss of customer trust and brand reputation.
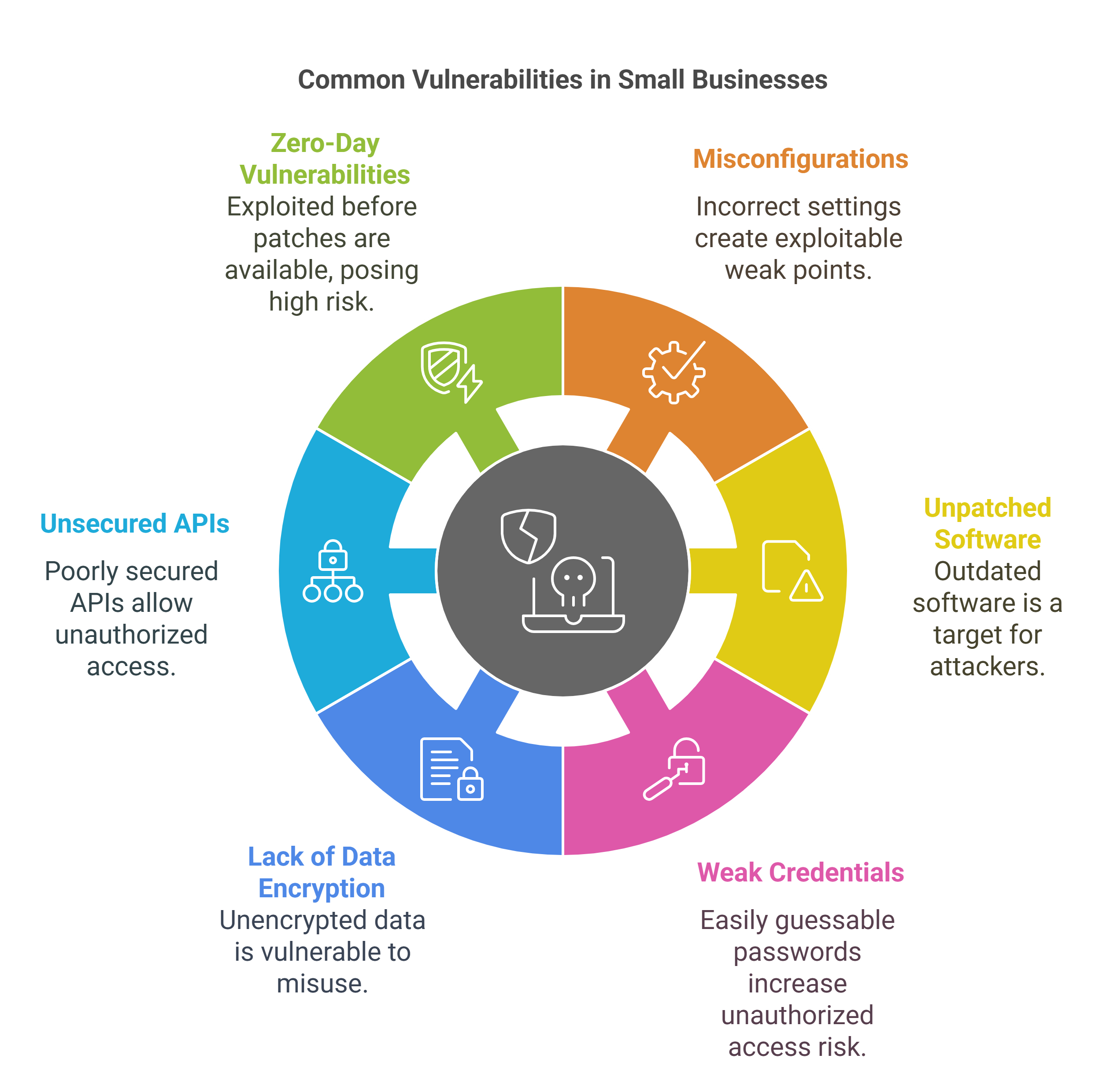
Common Vulnerabilities for Small Businesses:
-
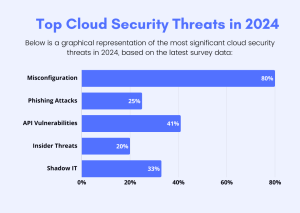
Misconfigurations: Incorrect settings in applications, databases, or network devices can create weak points that hackers can exploit.
-
Unpatched Software: Outdated software versions with known vulnerabilities can be targeted by attackers.
-
Weak Credentials: Using easily guessable passwords or reusing passwords across different systems increases the risk of unauthorized access.
-
Lack of Data Encryption: Storing sensitive data without encryption makes it easier for attackers to access and misuse it.
-
Unsecured APIs: APIs that are not properly secured can be exploited to gain unauthorized access to systems and data.
-
Zero-Day Vulnerabilities: These are vulnerabilities that are exploited before a patch is available, posing significant risks.
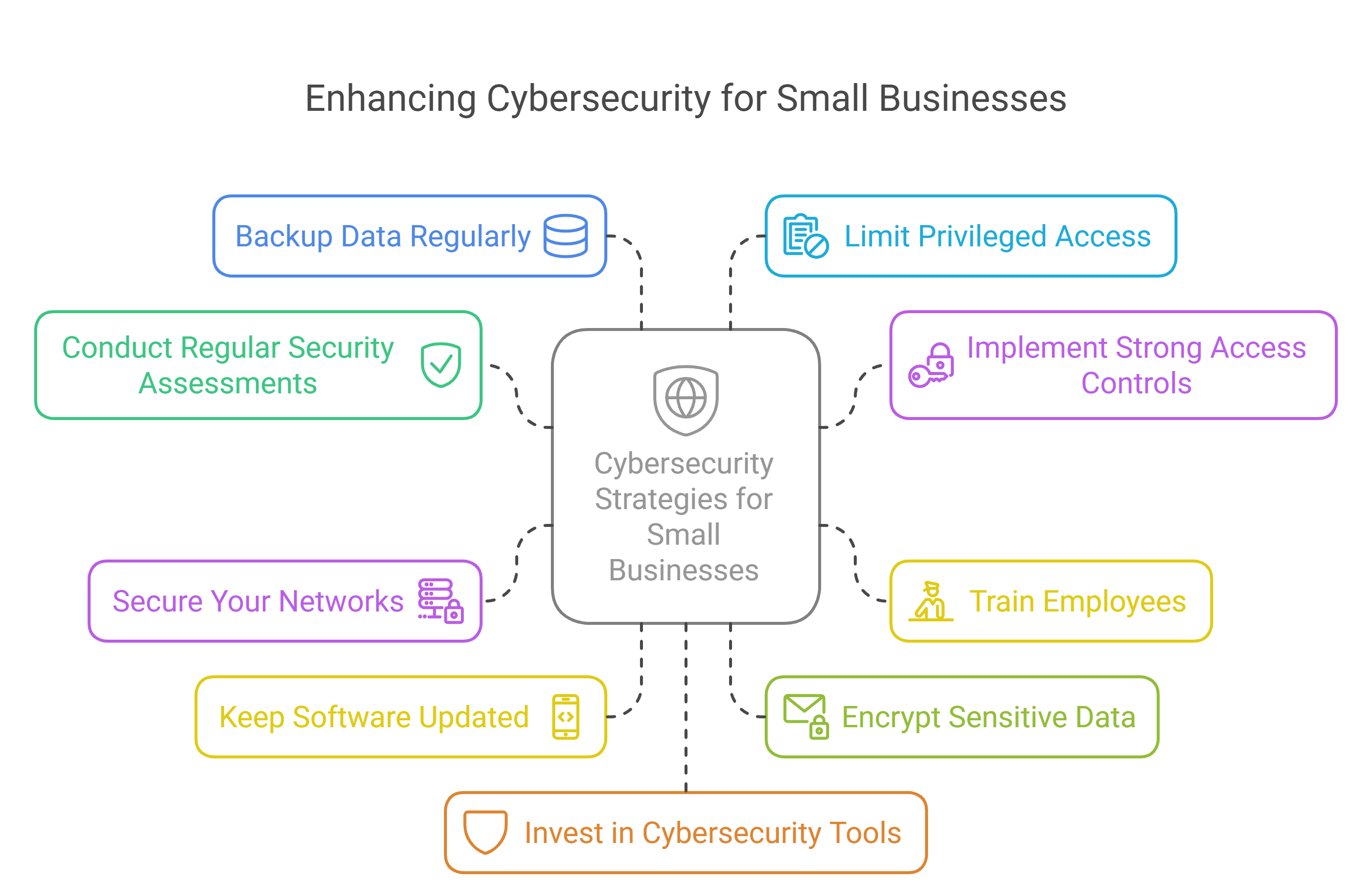
How Small Businesses Can Improve Security:
-
Conduct Regular Security Assessments: Evaluate your current cybersecurity posture to identify and address vulnerabilities.
-
Implement Strong Access Controls: Use role-based access control (RBAC) to limit access to sensitive information based on job roles. Enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of security.
-
Train Employees: Educate your staff on cybersecurity best practices, such as recognizing phishing emails, using strong passwords, and avoiding suspicious downloads.
-
Secure Your Networks: Encrypt your internet connection and use firewalls to protect your network. Ensure your Wi-Fi network is secure and hidden.
-
Keep Software Updated: Regularly update all software, including operating systems, web browsers, and applications. Enable automatic updates to ensure timely patching.
-
Encrypt Sensitive Data: Use encryption to protect sensitive data both in transit and at rest.
-
Backup Data Regularly: Maintain regular backups of critical data to ensure you can recover quickly in case of a cyberattack.
-
Limit Privileged Access: Restrict administrative privileges to essential personnel only. Regularly review and update access controls.
-
Invest in Cybersecurity Tools: Use antivirus software, intrusion detection systems, and other cybersecurity tools to monitor and protect your systems.
-
Develop an Incident Response Plan: Have a plan in place to respond quickly to security breaches. This should include steps for containment, eradication, and recovery.
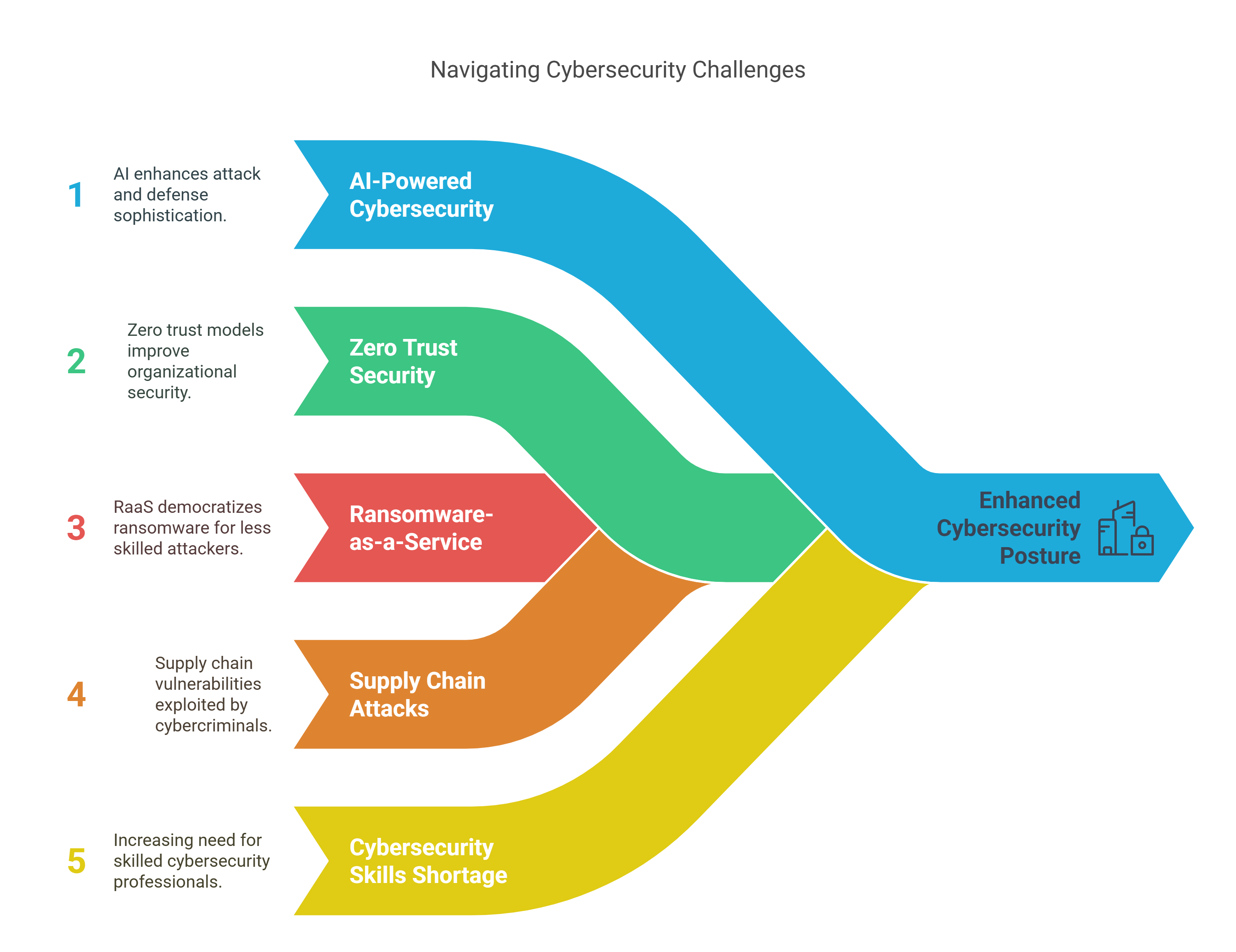
Latest Trends in Cybersecurity:
-
AI-Powered Cybersecurity: Both attackers and defenders are leveraging AI for more sophisticated attacks and defenses.
-
Increased Focus on Zero Trust Security: Organizations are adopting zero trust models to enhance security.
-
Rise of Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS): Ransomware attacks are becoming more accessible to less skilled attackers.
-
Supply Chain Attacks: Cybercriminals are targeting supply chains to exploit vulnerabilities in interconnected systems.
-
Cybersecurity Skills Shortage: There is a growing demand for skilled cybersecurity
By addressing these common vulnerabilities and implementing robust security measures, small businesses can significantly enhance their cybersecurity posture and protect against potential threats.