March 2025 Zero-Day Vulnerability Report

Introduction:
In March 2025, several critical zero-day vulnerabilities were identified and addressed by major software vendors, including Microsoft and Adobe. This report highlights the key vulnerabilities, their potential impacts, industry-specific insights, and practical advice for small businesses.
Microsoft Patches:
Microsoft released patches for 56 new CVEs, including six critical vulnerabilities and 50 important ones. Notably, six zero-day vulnerabilities were actively exploited in the wild. Key vulnerabilities include:
-
CVE-2025-26633: A security feature bypass in Microsoft Management Console, actively exploited.
-
CVE-2025-24985: A remote code execution vulnerability in the Windows Fast FAT File System Driver.
Adobe Patches:
Adobe addressed 37 CVEs across multiple products, including Acrobat Reader, Illustrator, and InDesign. Critical vulnerabilities in these products could allow attackers to execute arbitrary code.
Industry-Specific Data:
-
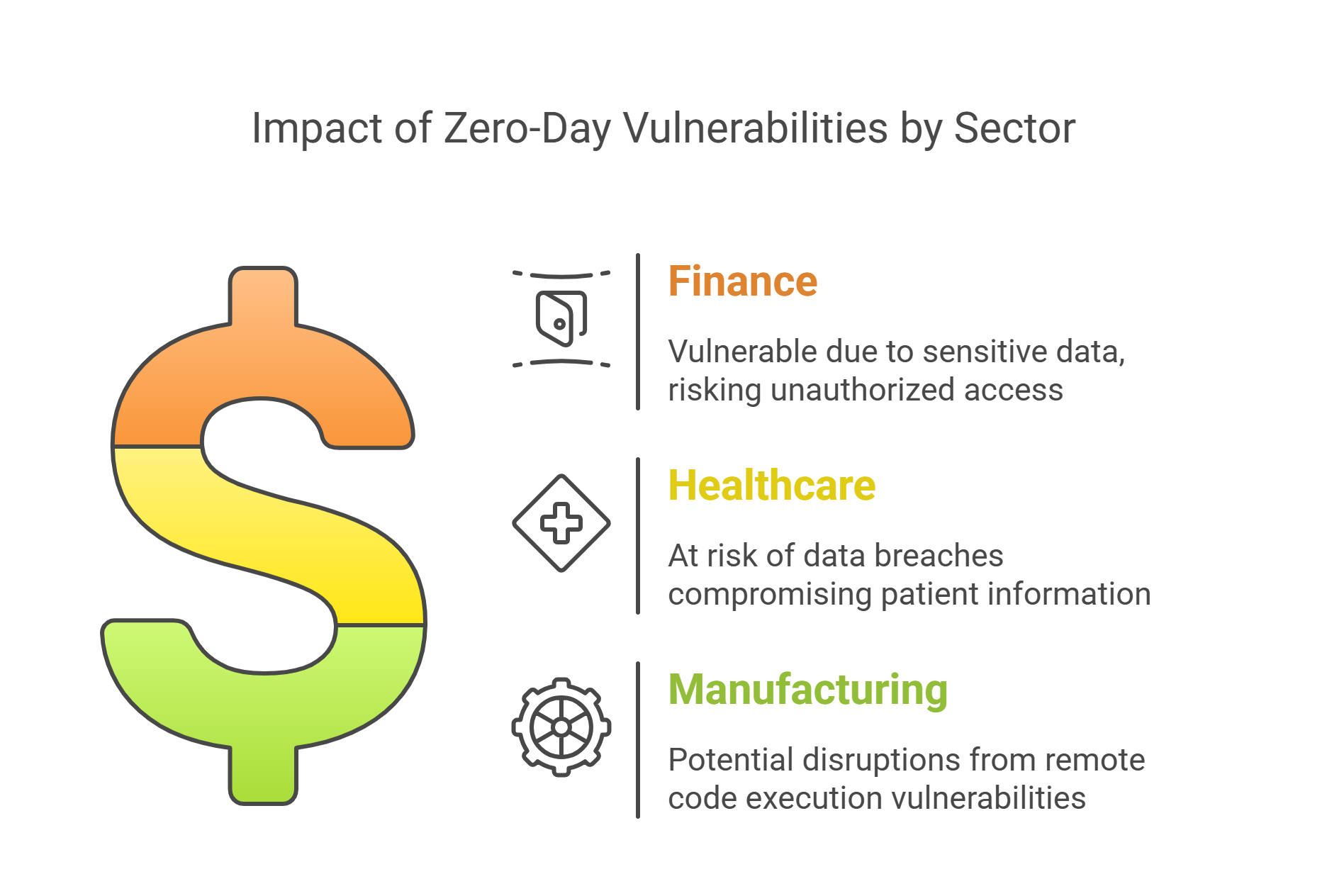
Finance: Financial institutions are particularly vulnerable to zero-day exploits due to the sensitive nature of their data. The CVE-2025-26633 vulnerability could allow attackers to bypass security features and gain unauthorized access to financial systems.
-
Healthcare: The healthcare sector, with its reliance on electronic health records, is at risk from vulnerabilities like CVE-2025-24985, which could lead to data breaches and compromise patient information.
-
Manufacturing: Manufacturing industries using Windows-based systems for automation and control could be affected by remote code execution vulnerabilities, potentially disrupting operations.
Implications of These Vulnerabilities:
Zero-day vulnerabilities pose significant risks as they are exploited before patches are available. The implications include:
-
Data Breaches: Unauthorized access to sensitive data.
-
Operational Disruption: Interruption of business operations and services.
-
Financial Loss: Costs associated with data breaches, including fines and remediation efforts.
-
Reputation Damage: Loss of customer trust and brand reputation.
Common Vulnerabilities for Small Businesses:
-
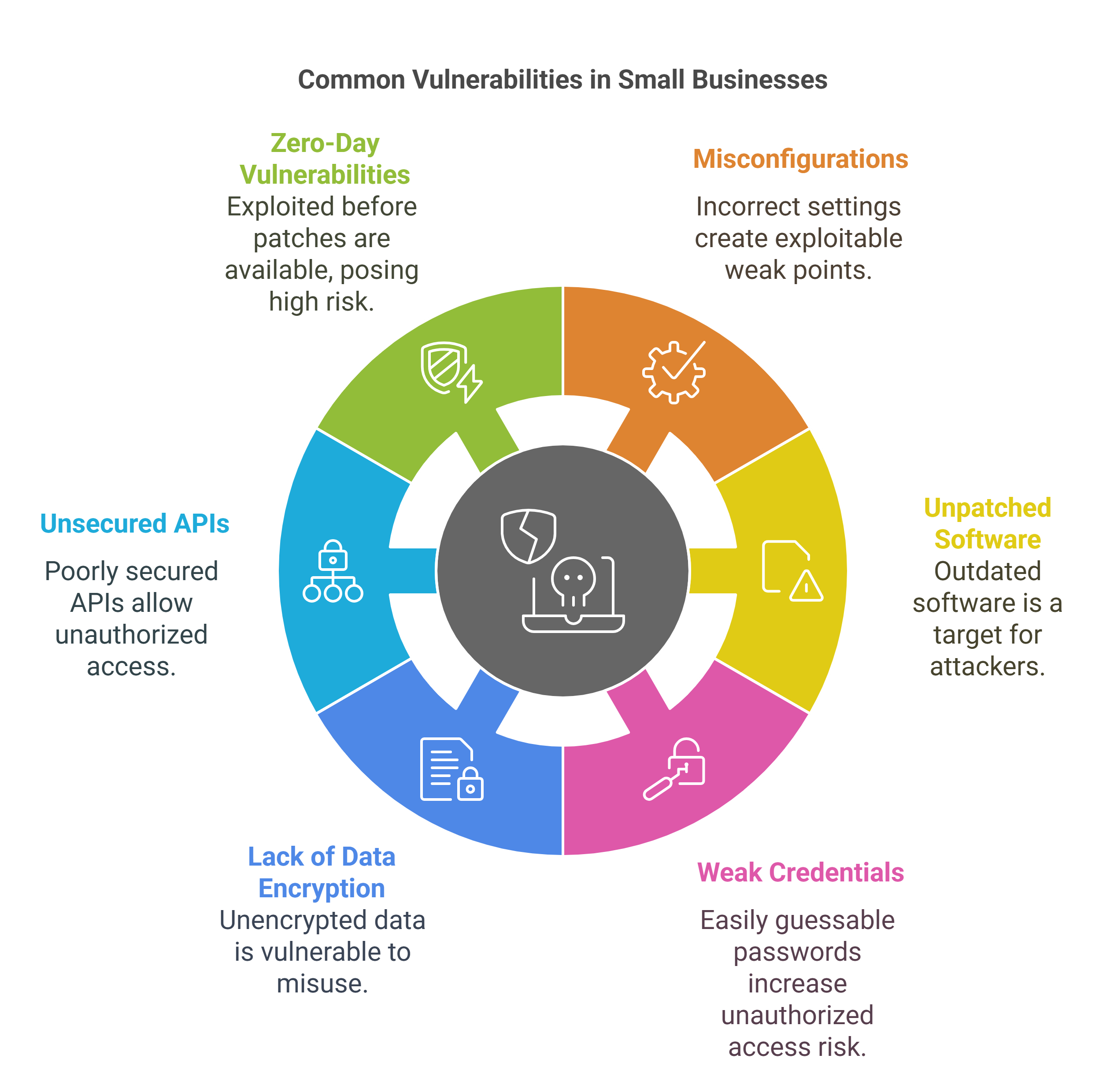
Misconfigurations: Incorrect settings in applications, databases, or network devices can create weak points that hackers can exploit.
-
Unpatched Software: Outdated software versions with known vulnerabilities can be targeted by attackers.
-
Weak Credentials: Using easily guessable passwords or reusing passwords across different systems increases the risk of unauthorized access.
-
Lack of Data Encryption: Storing sensitive data without encryption makes it easier for attackers to access and misuse it.
-
Unsecured APIs: APIs that are not properly secured can be exploited to gain unauthorized access to systems and data.
-
Zero-Day Vulnerabilities: These are vulnerabilities that are exploited before a patch is available, posing significant risks.
How Small Businesses Can Improve Security:
-
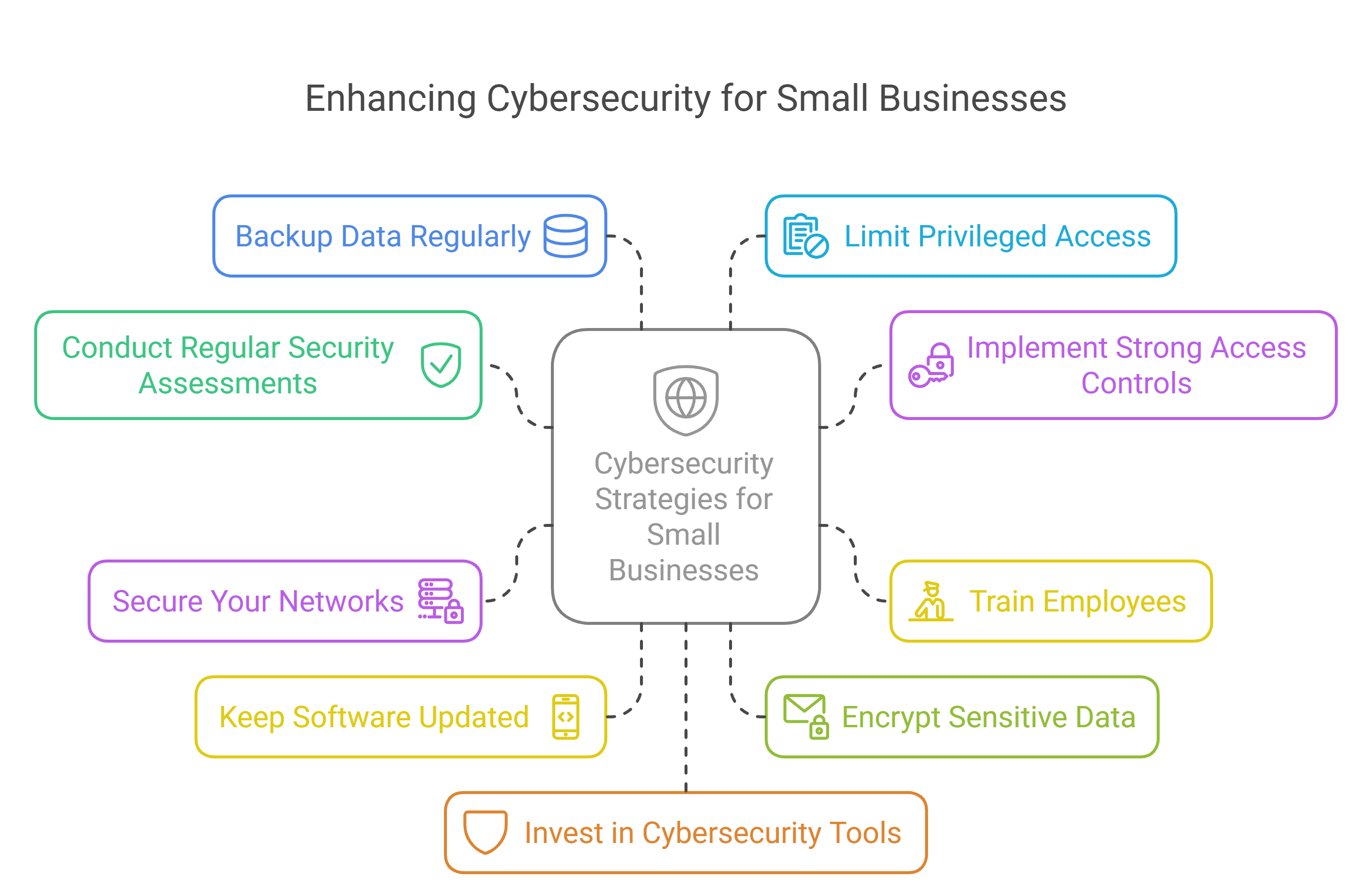
Conduct Regular Security Assessments: Evaluate your current cybersecurity posture to identify and address vulnerabilities.
-
Implement Strong Access Controls: Use role-based access control (RBAC) to limit access to sensitive information based on job roles. Enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of security.
-
Train Employees: Educate your staff on cybersecurity best practices, such as recognizing phishing emails, using strong passwords, and avoiding suspicious downloads.
-
Secure Your Networks: Encrypt your internet connection and use firewalls to protect your network. Ensure your Wi-Fi network is secure and hidden.
-
Keep Software Updated: Regularly update all software, including operating systems, web browsers, and applications. Enable automatic updates to ensure timely patching.
-
Encrypt Sensitive Data: Use encryption to protect sensitive data both in transit and at rest.
-
Backup Data Regularly: Maintain regular backups of critical data to ensure you can recover quickly in case of a cyberattack.
-
Limit Privileged Access: Restrict administrative privileges to essential personnel only. Regularly review and update access controls.
-
Invest in Cybersecurity Tools: Use antivirus software, intrusion detection systems, and other cybersecurity tools to monitor and protect your systems.
-
Develop an Incident Response Plan: Have a plan in place to respond quickly to security breaches. This should include steps for containment, eradication, and recovery.
Latest Trends in Cybersecurity:
-
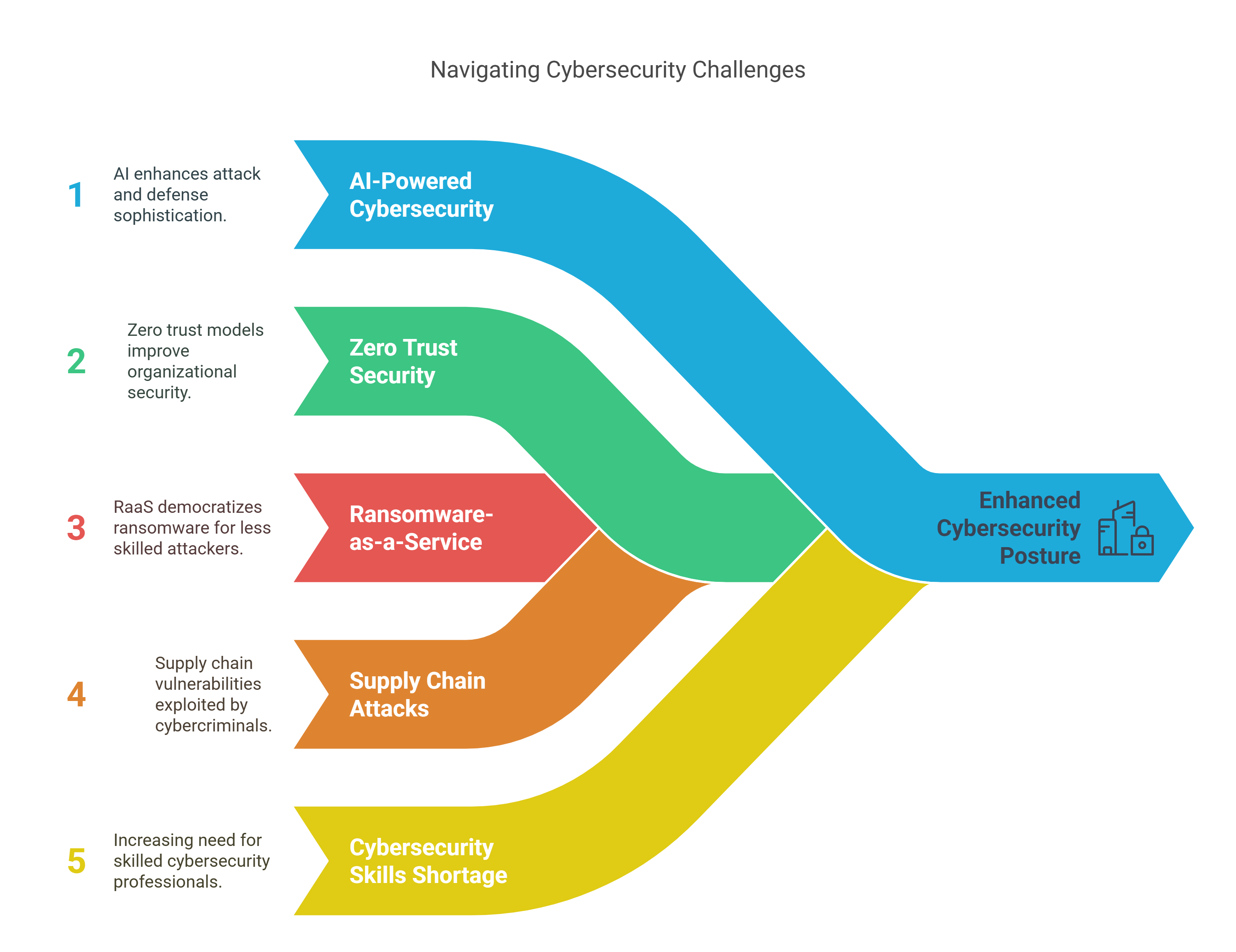
AI-Powered Cybersecurity: Both attackers and defenders are leveraging AI for more sophisticated attacks and defenses.
-
Increased Focus on Zero Trust Security: Organizations are adopting zero trust models to enhance security.
-
Rise of Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS): Ransomware attacks are becoming more accessible to less skilled attackers.
-
Supply Chain Attacks: Cybercriminals are targeting supply chains to exploit vulnerabilities in interconnected systems.
-
Cybersecurity Skills Shortage: There is a growing demand for skilled cybersecurity
By addressing these common vulnerabilities and implementing robust security measures, small businesses can significantly enhance their cybersecurity posture and protect against potential threats.

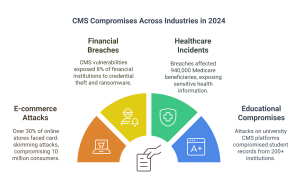
 In today’s digital landscape, every industry—from retail and finance to healthcare and education—relies on Content Management Systems (CMS) to manage data, streamline operations, and interact with customers. However, as reliance on these systems grows, so do the risks. Cyberattacks targeting CMS platforms have become a significant concern, making CMS hardening and regular security assessments essential for all businesses.
Alarming Trends in CMS Compromises Across Industries in 2024
Recent reports show that cybercriminals are increasingly targeting CMS platforms across industries. A survey conducted by Cybersecurity Ventures revealed:
In today’s digital landscape, every industry—from retail and finance to healthcare and education—relies on Content Management Systems (CMS) to manage data, streamline operations, and interact with customers. However, as reliance on these systems grows, so do the risks. Cyberattacks targeting CMS platforms have become a significant concern, making CMS hardening and regular security assessments essential for all businesses.
Alarming Trends in CMS Compromises Across Industries in 2024
Recent reports show that cybercriminals are increasingly targeting CMS platforms across industries. A survey conducted by Cybersecurity Ventures revealed: