by staatse | Apr 11, 2025 | API Security, Application Security, Cloud Security, CMS Security, Cybersecurity, IT Security Services, Network Security, Penetration Testing, Security Best Practices, Uncategorized, Vulnerability Management
Introduction:
In March 2025, several critical zero-day vulnerabilities were identified and addressed by major software vendors, including Microsoft and Adobe. This report highlights the key vulnerabilities, their potential impacts, industry-specific insights, and practical advice for small businesses.
Microsoft Patches:
Microsoft released patches for 56 new CVEs, including six critical vulnerabilities and 50 important ones. Notably, six zero-day vulnerabilities were actively exploited in the wild. Key vulnerabilities include:
-
CVE-2025-26633: A security feature bypass in Microsoft Management Console, actively exploited.
-
CVE-2025-24985: A remote code execution vulnerability in the Windows Fast FAT File System Driver.
Adobe Patches:
Adobe addressed 37 CVEs across multiple products, including Acrobat Reader, Illustrator, and InDesign. Critical vulnerabilities in these products could allow attackers to execute arbitrary code.
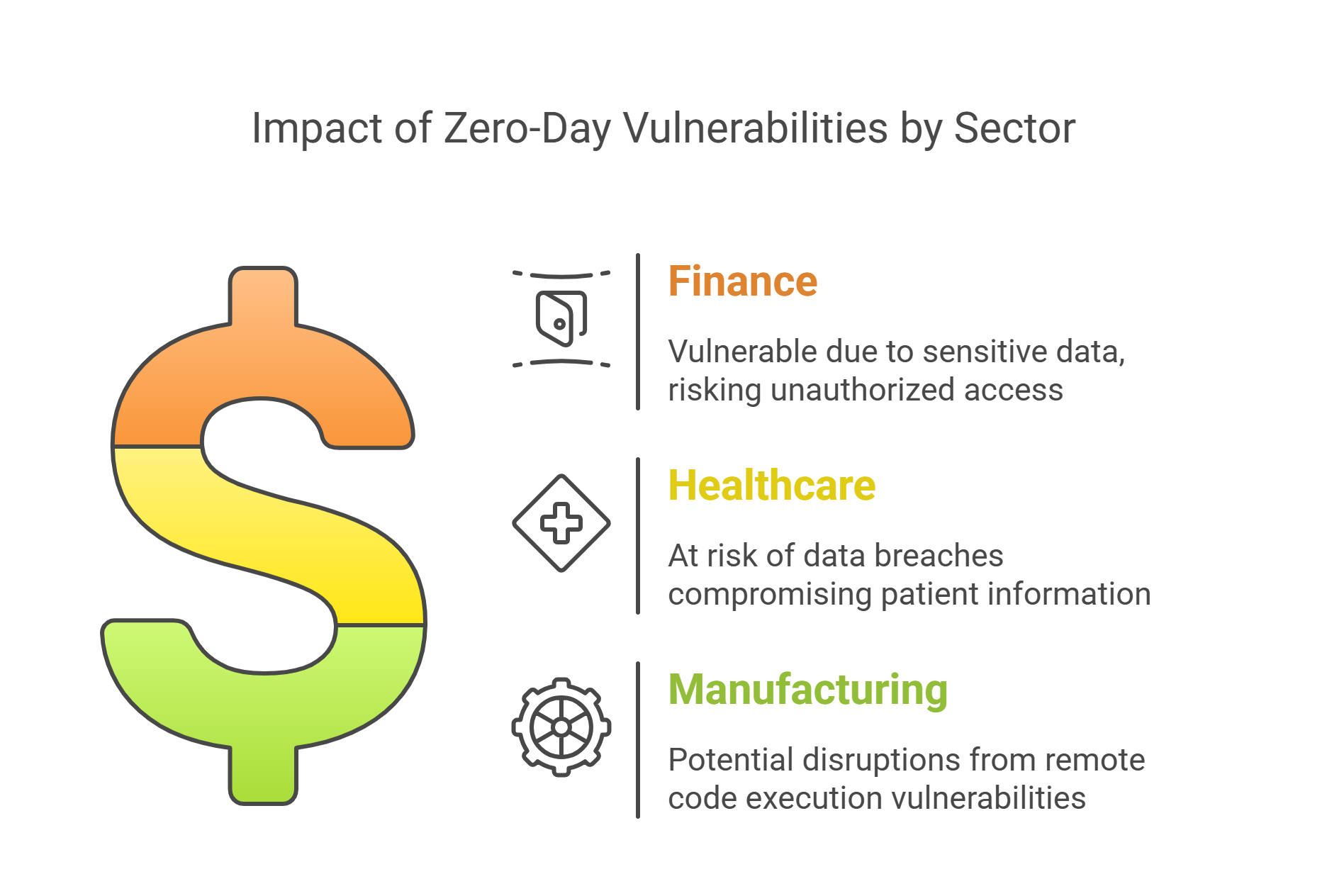
Industry-Specific Data:
-
Finance: Financial institutions are particularly vulnerable to zero-day exploits due to the sensitive nature of their data. The CVE-2025-26633 vulnerability could allow attackers to bypass security features and gain unauthorized access to financial systems.
-
Healthcare: The healthcare sector, with its reliance on electronic health records, is at risk from vulnerabilities like CVE-2025-24985, which could lead to data breaches and compromise patient information.
-
Manufacturing: Manufacturing industries using Windows-based systems for automation and control could be affected by remote code execution vulnerabilities, potentially disrupting operations.
Implications of These Vulnerabilities:
Zero-day vulnerabilities pose significant risks as they are exploited before patches are available. The implications include:
-
Data Breaches: Unauthorized access to sensitive data.
-
Operational Disruption: Interruption of business operations and services.
-
Financial Loss: Costs associated with data breaches, including fines and remediation efforts.
-
Reputation Damage: Loss of customer trust and brand reputation.
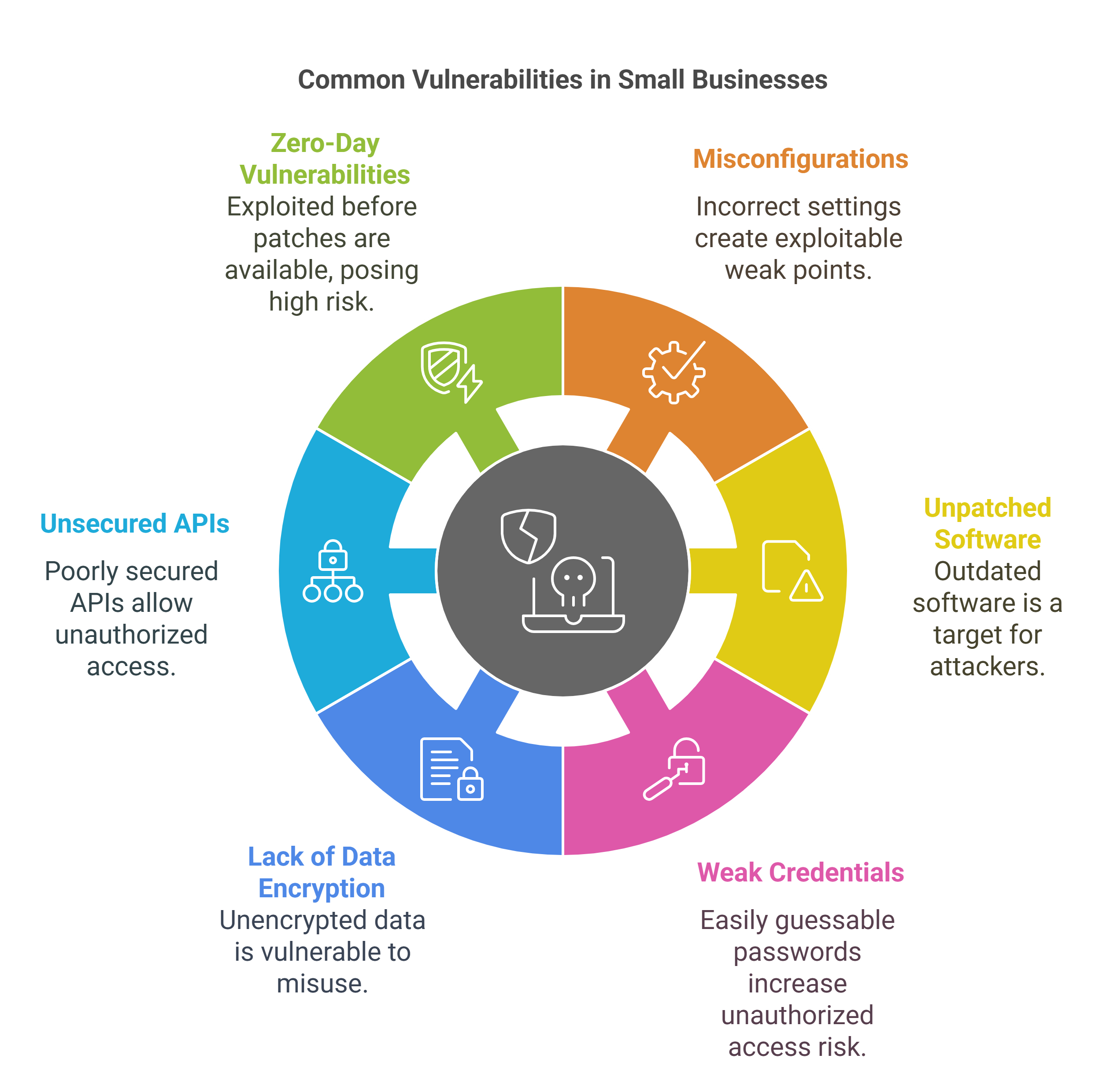
Common Vulnerabilities for Small Businesses:
-
Misconfigurations: Incorrect settings in applications, databases, or network devices can create weak points that hackers can exploit.
-
Unpatched Software: Outdated software versions with known vulnerabilities can be targeted by attackers.
-
Weak Credentials: Using easily guessable passwords or reusing passwords across different systems increases the risk of unauthorized access.
-
Lack of Data Encryption: Storing sensitive data without encryption makes it easier for attackers to access and misuse it.
-
Unsecured APIs: APIs that are not properly secured can be exploited to gain unauthorized access to systems and data.
-
Zero-Day Vulnerabilities: These are vulnerabilities that are exploited before a patch is available, posing significant risks.
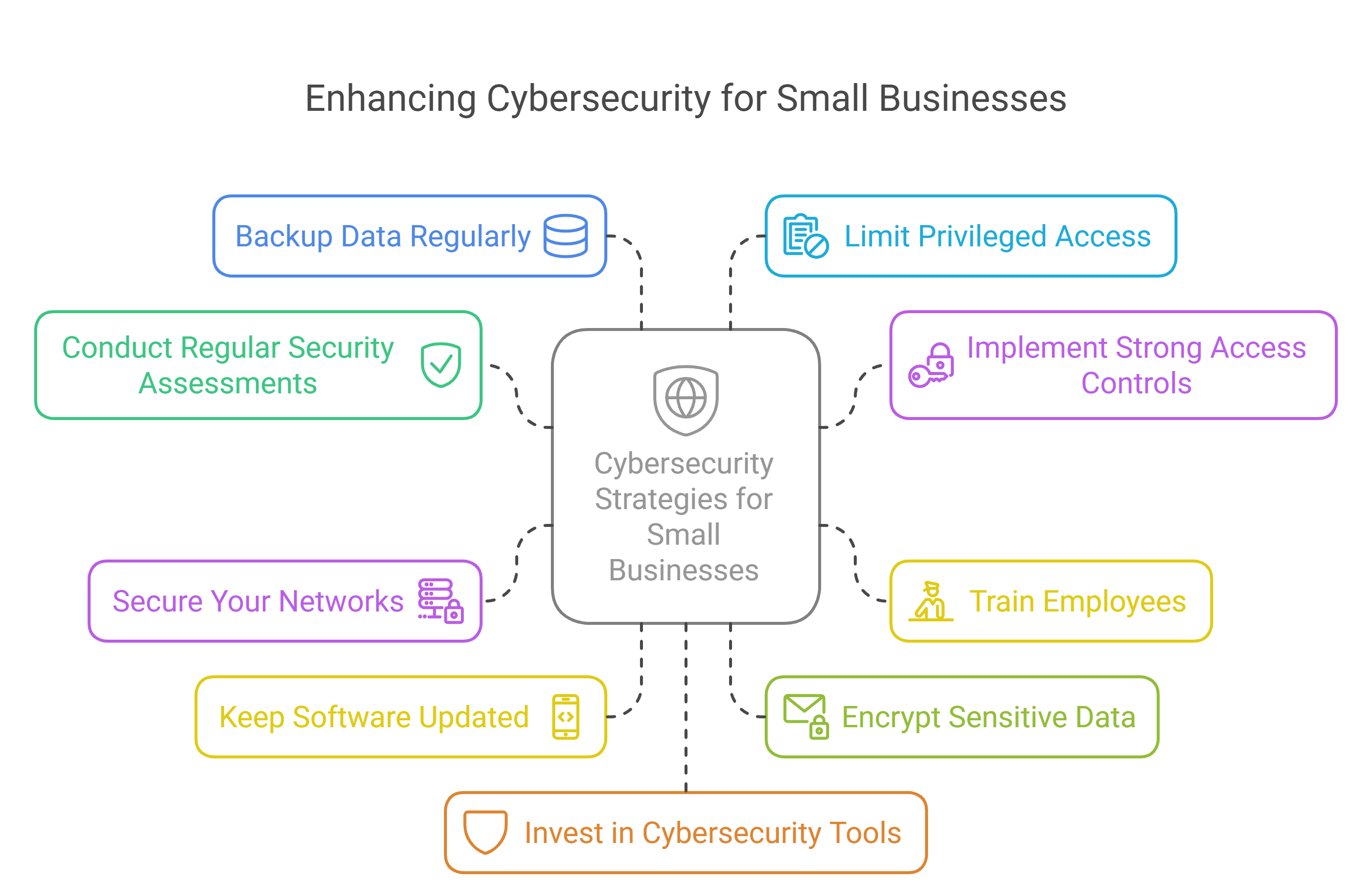
How Small Businesses Can Improve Security:
-
Conduct Regular Security Assessments: Evaluate your current cybersecurity posture to identify and address vulnerabilities.
-
Implement Strong Access Controls: Use role-based access control (RBAC) to limit access to sensitive information based on job roles. Enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of security.
-
Train Employees: Educate your staff on cybersecurity best practices, such as recognizing phishing emails, using strong passwords, and avoiding suspicious downloads.
-
Secure Your Networks: Encrypt your internet connection and use firewalls to protect your network. Ensure your Wi-Fi network is secure and hidden.
-
Keep Software Updated: Regularly update all software, including operating systems, web browsers, and applications. Enable automatic updates to ensure timely patching.
-
Encrypt Sensitive Data: Use encryption to protect sensitive data both in transit and at rest.
-
Backup Data Regularly: Maintain regular backups of critical data to ensure you can recover quickly in case of a cyberattack.
-
Limit Privileged Access: Restrict administrative privileges to essential personnel only. Regularly review and update access controls.
-
Invest in Cybersecurity Tools: Use antivirus software, intrusion detection systems, and other cybersecurity tools to monitor and protect your systems.
-
Develop an Incident Response Plan: Have a plan in place to respond quickly to security breaches. This should include steps for containment, eradication, and recovery.
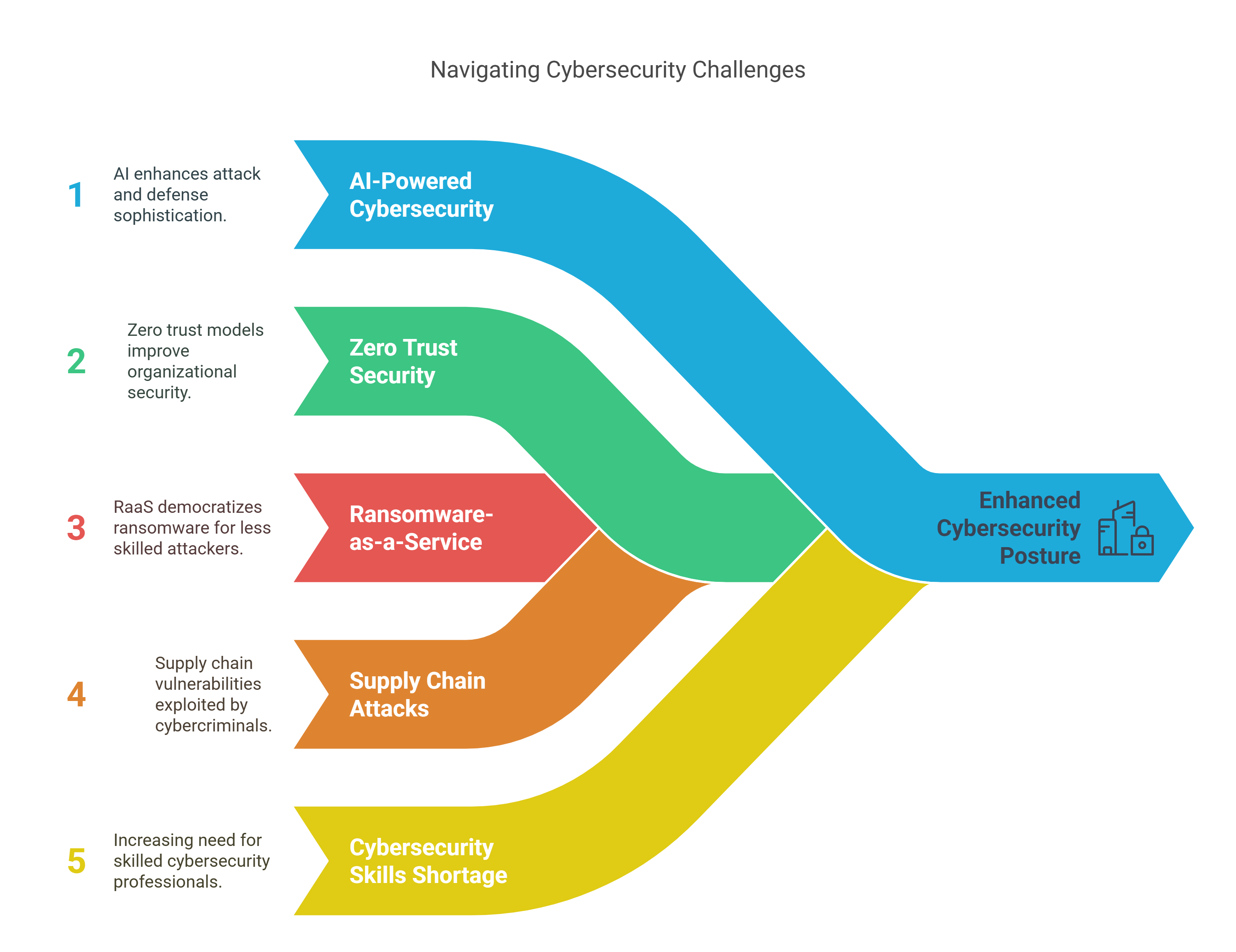
Latest Trends in Cybersecurity:
-
AI-Powered Cybersecurity: Both attackers and defenders are leveraging AI for more sophisticated attacks and defenses.
-
Increased Focus on Zero Trust Security: Organizations are adopting zero trust models to enhance security.
-
Rise of Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS): Ransomware attacks are becoming more accessible to less skilled attackers.
-
Supply Chain Attacks: Cybercriminals are targeting supply chains to exploit vulnerabilities in interconnected systems.
-
Cybersecurity Skills Shortage: There is a growing demand for skilled cybersecurity
By addressing these common vulnerabilities and implementing robust security measures, small businesses can significantly enhance their cybersecurity posture and protect against potential threats.
by staatse | Sep 19, 2024 | Application Security, Cybersecurity, Network Security, Penetration Testing, Vulnerability Management
In today’s digital landscape, businesses of all sizes depend heavily on technology to manage operations, store sensitive data, and engage with customers. This reliance, however, also increases the risk of cyber threats. To protect your business from potential attacks and data breaches, it’s crucial to implement strong security measures, and penetration testing is a key component of this defense strategy. But why is penetration testing so essential for your business? Let’s explore.
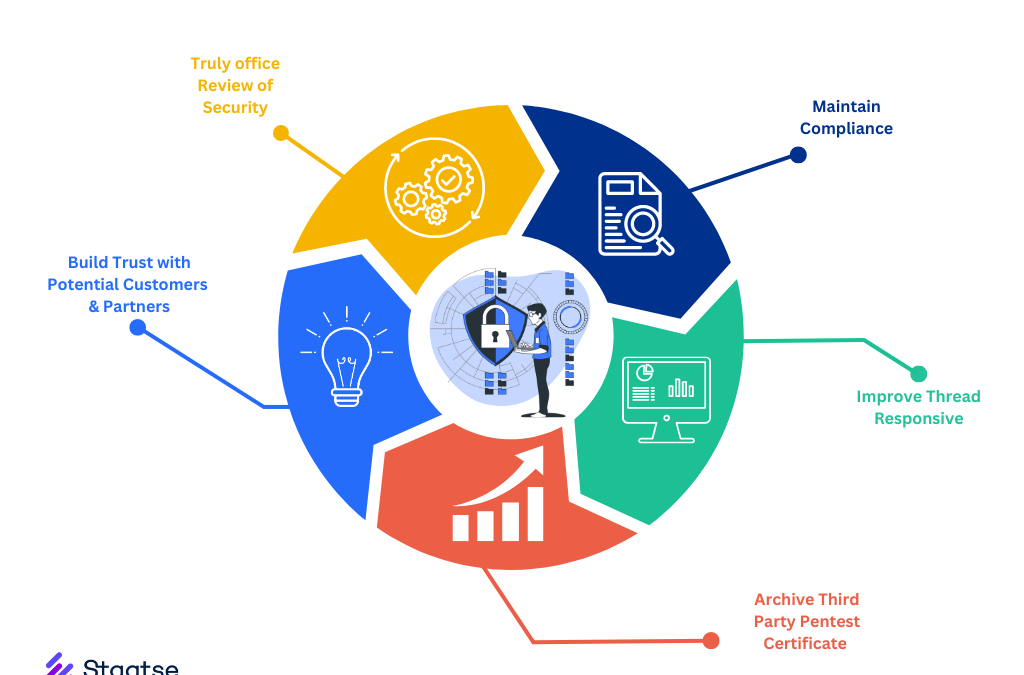
1. Identifying Vulnerabilities Before Attackers Do
- Proactive Detection: By simulating real-world attack scenarios, penetration testing can reveal vulnerabilities such as outdated software, weak passwords, or unsecured endpoints that cybercriminals could exploit.
- Comprehensive Assessment: It goes beyond traditional security measures, providing a thorough evaluation of your digital environment’s resilience against sophisticated attacks.
2. Enhancing Security Measures and Reducing Risk
Once vulnerabilities are identified, your business can take proactive steps to address these weaknesses. This not only strengthens your defenses but also reduces the risk of a successful cyberattack, protecting your sensitive data and maintaining business continuity.
- Tailored Security Improvements: Based on the findings, you can implement specific security measures such as applying patches, updating configurations, or enhancing monitoring practices.
- Risk Mitigation: Understanding the potential impact of each vulnerability allows you to prioritize and address the most critical issues first, reducing the overall risk to your organization.
3. Ensuring Compliance with Industry Regulations
Many industries are governed by strict regulatory standards, such as GDPR for data protection, HIPAA for healthcare, and PCI-DSS for payment card security. These regulations often require regular security assessments, including penetration testing, to ensure that sensitive information is adequately protected.
- Meeting Compliance Requirements: Regular penetration testing helps demonstrate your commitment to maintaining a high level of security and ensures that your business complies with industry-specific regulations.
- Avoiding Legal and Financial Penalties: Failing to comply with these regulations can result in significant fines and legal consequences. Penetration testing helps you avoid such risks by identifying and addressing potential compliance gaps.
4. Protecting Your Reputation and Building Trust
A data breach can have a devastating impact on your company’s reputation, leading to loss of customer trust, reduced revenue, and long-term damage to your brand. Penetration testing is a proactive measure that shows your commitment to cybersecurity, helping to build trust with customers, partners, and stakeholders.
- Customer Confidence: By proactively securing your systems, you reassure customers that their data is safe and that your business is a trustworthy partner.
- Brand Protection: Preventing breaches before they occur helps safeguard your brand’s reputation, avoiding the negative publicity and loss of trust associated with security incidents.
How to Implement Penetration Testing: A Step-by-Step Guide
1. Define Clear Objectives
Identify what you aim to achieve with penetration testing. Are you focusing on a specific application, network segment, or your entire IT infrastructure? Clearly defining your goals will help tailor the testing to your specific needs and ensure meaningful results.
2. Choose the Right Testing Approach
There are different methodologies to choose from:
- Black Box Testing: The tester has no prior knowledge of the system, simulating an external attack.
- White Box Testing: The tester has full access to the system’s architecture and source code, allowing for a comprehensive security evaluation.
- Gray Box Testing: The tester has partial knowledge of the system, representing a scenario where an insider or semi-privileged user might attack.
Select the approach that best aligns with your security objectives and budget.
3. Select a Reliable Penetration Testing Provider
Choose a reputable provider with experience in your industry. Look for a company that offers a structured approach, detailed reporting, and a clear plan for post-testing support. Ask for case studies or references to ensure they have a proven track record.
4. Conduct the Testing
During the testing phase, the penetration testing team will simulate attacks on your systems, identifying vulnerabilities and assessing their potential impact. They will then provide a comprehensive report detailing the findings, along with recommendations for remediation.
5. Address and Mitigate Vulnerabilities
The final step is to act on the findings from the penetration test. This might involve applying security patches, updating configurations, revising access controls, or implementing additional security measures. Regular follow-up testing can ensure that these vulnerabilities have been effectively addressed.
Conclusion
Penetration testing is a strategic investment that helps protect your business from the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats. By proactively identifying and addressing security vulnerabilities, you not only enhance your defenses but also ensure compliance with industry regulations, protect your reputation, and build trust with your customers. In a digital world where security breaches are increasingly common, penetration testing is a crucial tool for maintaining a secure and resilient business environment.